Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
片岡 隆浩*; 直江 翔太*; 村上 海斗*; 雪峰 諒平*; 藤本 有希*; 神崎 訓枝; 迫田 晃弘; 光延 文裕*; 山岡 聖典*
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 70(2), p.154 - 159, 2022/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:57.52(Nutrition & Dietetics)Radon therapy has been reported to be effective in the management of rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease caused by immune cell imbalance. Although there are several reports that suggest that radon therapy induces Th17 cells, there are no studies on the effects of radon inhalation on Th1, Th2, and Th17 immune balance. The aim of this study, therefore, was to examine the changes in cytokine levels after radon inhalation. BALB/c mice were subjected to radon inhalation at a concentration of 2000 Bq/m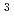 for 2 or 4 weeks, whereas SKG/Jcl mice were subjected to radon inhalation at a concentration of 2000 Bq/m
for 2 or 4 weeks, whereas SKG/Jcl mice were subjected to radon inhalation at a concentration of 2000 Bq/m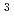 for 4 weeks after zymosan administration. For example, the results showed that radon inhalation for 4 weeks not only activated Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells but also modulated immune balance. This suggests that radon inhalation has different mechanisms of action in SKG/Jcl mice and normal BABL/c mice and that radon inhalation has immunomodulatory effects.
for 4 weeks after zymosan administration. For example, the results showed that radon inhalation for 4 weeks not only activated Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells but also modulated immune balance. This suggests that radon inhalation has different mechanisms of action in SKG/Jcl mice and normal BABL/c mice and that radon inhalation has immunomodulatory effects.
 and CaCl
and CaCl
茶竹 俊行*; 角南 智子
Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 124, p.15 - 25, 2013/07
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:60.13(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)In this study, crystals of Z-DNA hexamer d(CGCGCG) complexed with MgCl and CaCl
and CaCl were obtained in the presence of high concentrations of alkaline earth salts (500 mM) using a temperature control technique, and their crystal structures were determined at 1.3
were obtained in the presence of high concentrations of alkaline earth salts (500 mM) using a temperature control technique, and their crystal structures were determined at 1.3 resolution. Mg
resolution. Mg and Ca
and Ca cations in these structures tend to interact directly with phosphate groups of Z-DNA duplexes; however, they tend to form water-mediated interactions with Z-DNA in the presence of lower concentrations of alkaline earth salts. In these crystals, a DNA duplex was laid along its c-axis and interacted with its 6 neighboring DNA duplexes through coordination bonds of P-O...(Mg
cations in these structures tend to interact directly with phosphate groups of Z-DNA duplexes; however, they tend to form water-mediated interactions with Z-DNA in the presence of lower concentrations of alkaline earth salts. In these crystals, a DNA duplex was laid along its c-axis and interacted with its 6 neighboring DNA duplexes through coordination bonds of P-O...(Mg or Ca
or Ca )...O-P. A symmetrical hexagonal Z-DNA duplex assembly model may explain DNA condensation caused by alkaline earth salts. These structures offer insights into the functions of alkaline earth cations essential to the structures and assembly of Z-DNA duplexes.
)...O-P. A symmetrical hexagonal Z-DNA duplex assembly model may explain DNA condensation caused by alkaline earth salts. These structures offer insights into the functions of alkaline earth cations essential to the structures and assembly of Z-DNA duplexes.
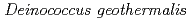
Sghaier, H.*; 佐藤 勝也; 大庭 寛史*; 鳴海 一成
African Journal of Biochemistry Research, 4(4), p.111 - 118, 2010/04
The moderately thermophilic bacterium 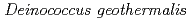 exhibits extraordinary resistance to ionizing radiation. RecA protein is considered to be one of the most important participants in radioresistance. To assess the role of the RecA protein in
exhibits extraordinary resistance to ionizing radiation. RecA protein is considered to be one of the most important participants in radioresistance. To assess the role of the RecA protein in  , the
, the  gene was isolated from
gene was isolated from  and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. After the
and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. After the  RecA protein (GeoRecA) was purified, the recombination activity was investigated
RecA protein (GeoRecA) was purified, the recombination activity was investigated  . GeoRecA most efficiently promoted the strand exchange reaction between homologous linear double-stranded DNA and circular single-stranded DNA substrates at 50
. GeoRecA most efficiently promoted the strand exchange reaction between homologous linear double-stranded DNA and circular single-stranded DNA substrates at 50 C. Like
C. Like  RecA protein (DraRecA), GeoRecA could promote DNA strand exchange reaction
RecA protein (DraRecA), GeoRecA could promote DNA strand exchange reaction 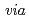 normal and inverse pathways. Furthermore, GeoRecA complemented the RecA deficiency of
normal and inverse pathways. Furthermore, GeoRecA complemented the RecA deficiency of  . These results indicate that GeoRecA is a functional homologue of DraRecA and plays an important role in radioresistance. However, unlike DraRecA, GeoRecA could not complement the RecA deficiency of
. These results indicate that GeoRecA is a functional homologue of DraRecA and plays an important role in radioresistance. However, unlike DraRecA, GeoRecA could not complement the RecA deficiency of  , suggesting that GeoRecA require more strict intracellular conditions than DraRecA does to fulfill its function.
, suggesting that GeoRecA require more strict intracellular conditions than DraRecA does to fulfill its function.

佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 菊地 正博; 北山 滋; 柳沢 忠*; 山本 和生; 渡辺 宏
Journal of Biochemistry, 131(1), p.121 - 129, 2002/01
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:38.61(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)これまでデイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスRecAは,大腸菌とは異なり特別な機能を有しているのではないかと考えられてきた。本論文ではラジオデュランスの野生型及び2種類の変異型RecAを解析し,ラジオデュランスRecAが大腸菌RecAと同等の機能を有していること、当該菌の放射線抵抗性にはRecAによるDNA組換え活性よりも、co-protease活性の方がより重要な役割を担っていることを示した。